AI+automation - the future path of bioreactors: from precision fermentation to smart pharmaceuticals

Nowadays, AI and automation are driving the upgrade of this core capability: not only continuing the precise control in the pharmaceutical field, but also expanding it to precise fermentation scenarios such as food protein and biomaterials, solving the new demand for "large-scale+low-cost".
1、 Automation: the foundation of biomanufacturing
Biological manufacturing relies on the metabolic output of living cells, and even slight deviations in parameters such as temperature, nutrition, and inoculation accuracy can lead to failure.
The core role of automation technology is to reduce errors through "standardized control" and lay the foundation for subsequent optimization.
Bruce Li from TJX Bioengineering categorizes automation into two types:
Process automation: Since the 1950s and 1960s, real-time data such as temperature, nutrient levels, and exhaust gas composition have been collected through sensors, and the reactors are controlled by computers to solve the problem of "unstable basic conditions";
Workflow automation: In the past decade, robotic arm technology has been applied to replace manual completion of repetitive operations such as liquid inoculation and metering, solving the pain point of "insufficient manual operation accuracy".
These two types of technologies not only shift biomanufacturing from "experience based" to "controllable", but also accumulate preliminary process data - and these data are the "raw materials" for AI's deep intervention.
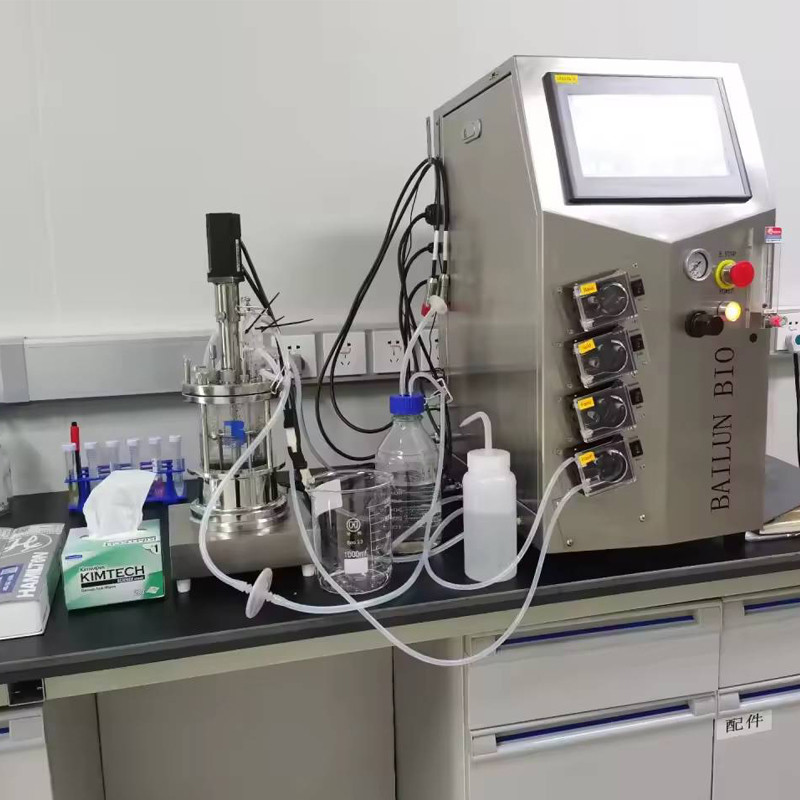

2、 High throughput+AI: filling the gap of "data scarcity"
Although traditional automation can stably control reactor conditions, it cannot achieve "precise optimization based on data":
AI needs to predict production and adjust parameters through historical and real-time data, provided that there is enough "success or failure case data", which was once a long-term bottleneck in the industry.
The emergence of high-throughput parallel bioreactors has completely broken the data deadlock: it can simultaneously test different conditions in multiple independent tanks and generate 64 data points in a week (compared to the past where four PhDs shared one reactor and could only accumulate 5-6 data points in a year).
Massive data combined with AI algorithms has finally enabled the theoretical implementation of "predictive model control" from the 1990s - by analyzing data to deduce optimal growth and production conditions, achieving autonomous optimization of reactors.
It can be said that high-throughput solves the problem of "where data comes from" and AI solves the problem of "how data is used". The combination of the two enables biomanufacturing to move from "stable control" to "precise optimization".
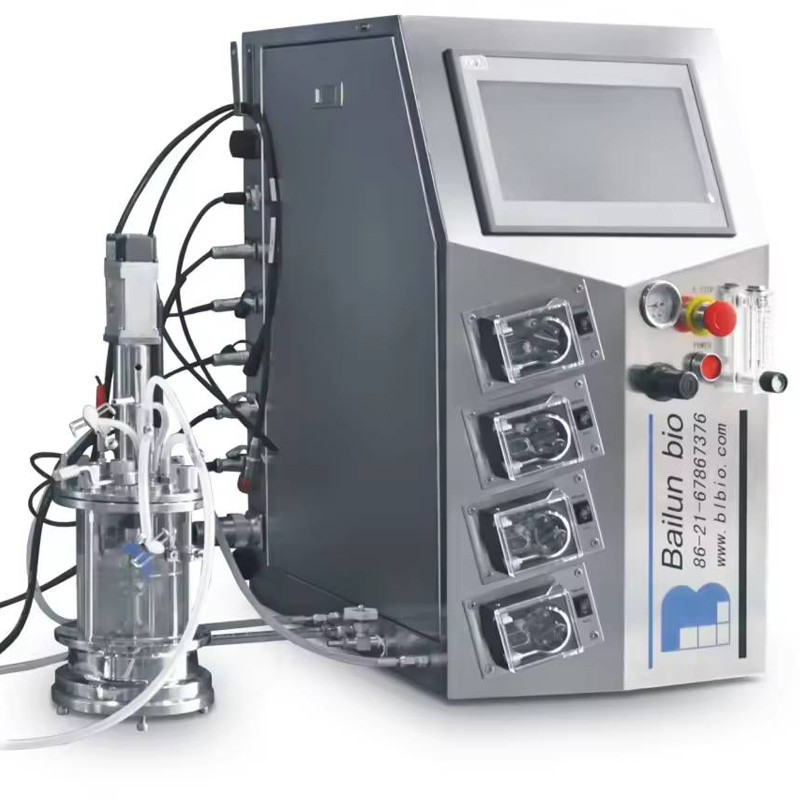

3、 Continuous Fermentation+AI: From "Laboratory Optimization" to "Mass Production Implementation"
If high-throughput+AI focuses on optimizing efficiency in the laboratory stage, then continuous fermentation+AI aims for breakthroughs in efficiency in the mass production stage - after all, the optimization results in the laboratory need to be transformed into stable production capacity in actual production.
Bailun has designed a targeted "dual tank continuous fermentation system": one tank focuses on cell growth, and the other tank focuses on product generation, solving the pollution and genetic drift problems of traditional continuous systems from the root;
On this basis, AI software can continuously monitor the fermentation process for multiple weeks and adjust parameters in real-time.

The breakthrough brought by this combination is obvious:
The production capacity of a single tank is comparable to the output of multiple tanks, usually achieving a productivity increase of 2-10 times while reducing capital and operating costs - this is the core solution for the "large-scale, low-cost" demand of precision fermentation, making technological achievements truly marketable.
4、 Fully Automated Fermentation: A Realistic Balance between Efficiency and Risk
Even though AI+automation has covered multiple stages from control, optimization to mass production, "fully automated operation" is still not common in practice.
The core reason lies in the risk cost: a batch of fermentation failures can result in hundreds of thousands of dollars in losses, so the industry generally sets up "hold points" - allowing engineers to verify key steps before the process progresses and confirm their correctness before continuing.