Billion dollar track | Microbial fermentation method of hyaluronic acid

Hyaluronic acid (HA), also known as hyaluronic acid, is a linear polysaccharide formed by alternating connections of N-acetylglucosamine and D-glucuronic acid. It is widely present in human skin, joints, and other tissues, and has excellent moisturizing, repairing, and anti-aging functions.
1、 Medical beauty application scenarios
Small molecule HA (<500kDa): infiltrates into the dermis, promotes collagen regeneration, and is used for deep water supplement such as Shuiguang needle and essence liquid to improve dryness and fine lines. The effect lasts for 4-6 months.
Medium molecular weight HA (500-1500kDa): with a slightly soft texture, it fills soft tissues such as tear troughs and temples, and also has anti-inflammatory effects, lasting 6-12 months.
High molecular weight HA (>1500kDa): forms a physical support network for deep filling such as nose augmentation and buttock augmentation, improving contour stability, and the effect can last for 12-18 months.
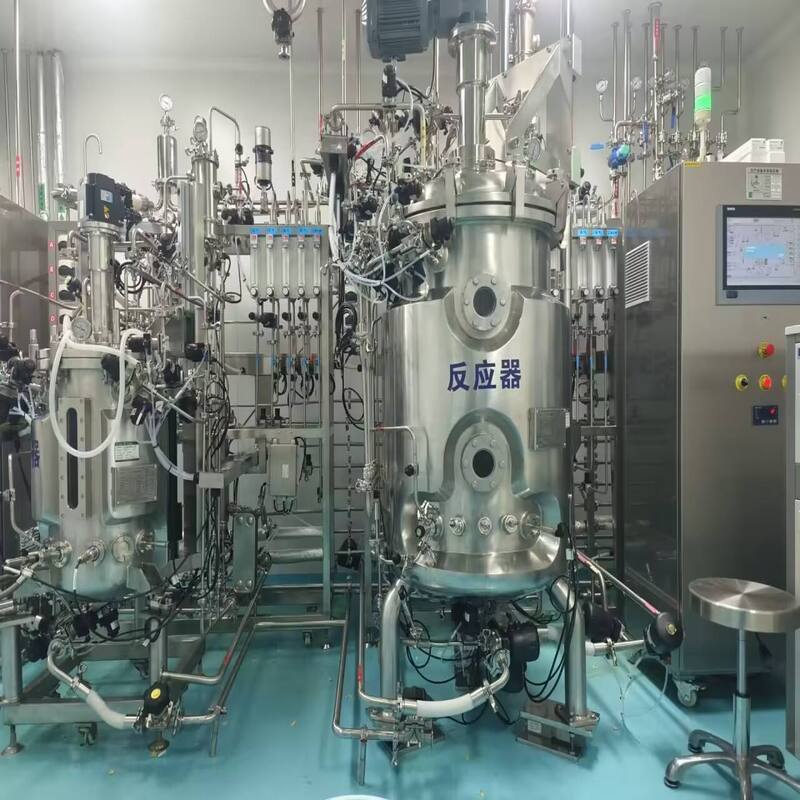

2、 Breakthrough in Microbial Fermentation
The core of preparing hyaluronic acid (HA, commonly known as hyaluronic acid) through a bioreactor is microbial fermentation. The commonly used HA producing strain is Streptococcus suis, and the process can be briefly divided into four key steps:
1. Preparation of bacterial strains
Screening or genetically engineering high-yield and safe strains (such as optimizing HA synthase genes to improve yield), first cultivate the "seed liquid" in a shake flask (ensuring bacterial activity and concentration) to prepare for subsequent reactor fermentation.
2. Preparation of culture medium and inoculation into the reactor: Add customized culture medium (core components: carbon source such as glucose/sucrose, nitrogen source such as yeast extract/peptone, minerals such as Mg ² ⁺/Mn ² ⁺) to the bioreactor, sterilize it, add seed liquid, and start fermentation.
3. Control of bioreactor fermentation by regulating key parameters in the reactor to promote the production of HA by bacterial cells:
Temperature: 30-37 ℃ (suitable for streptococcal growth); PH: Maintain 7.0-7.5 (adjust in real-time with acid-base solution to avoid affecting enzyme activity);

Dissolved oxygen content: oxygen demand in the early stage (bacterial proliferation), moderate oxygen control in the later stage (promoting HA synthesis, HA is an extracellular polysaccharide that needs to be secreted into the fermentation broth);
Mixing: Low speed mixing ensures the uniformity of the material and avoids damaging the bacterial cells. The fermentation cycle is usually 12-48 hours.
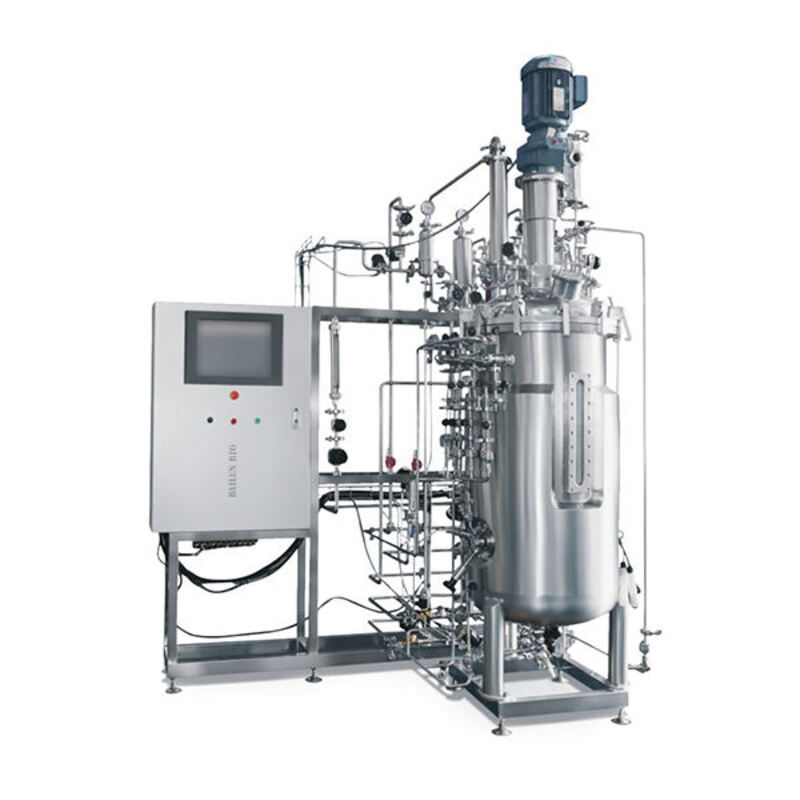

4. Separation and purification
After fermentation, remove bacteria and impurities by centrifugation/filtration, add ethanol (or isopropanol) to the filtrate to precipitate HA (polysaccharide can be separated by alcohol), and then desalting (ion exchange resin), decoloring (activated carbon), freeze drying/spray drying to obtain pure hyaluronic acid powder.
In 2023, the market size of HA raw materials in China will reach 4.71 billion yuan, and it is expected to exceed 10 billion yuan by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of over 20%. The medical beauty field accounts for 47.5%, and injection products contribute 2.5%.