Five popular traditional Chinese medicines undergo liquid fermentation, including Sanghuang, Dendrobium, Poria cocos, Ginseng, and Cordyceps, transforming from "rare" to "affordable"

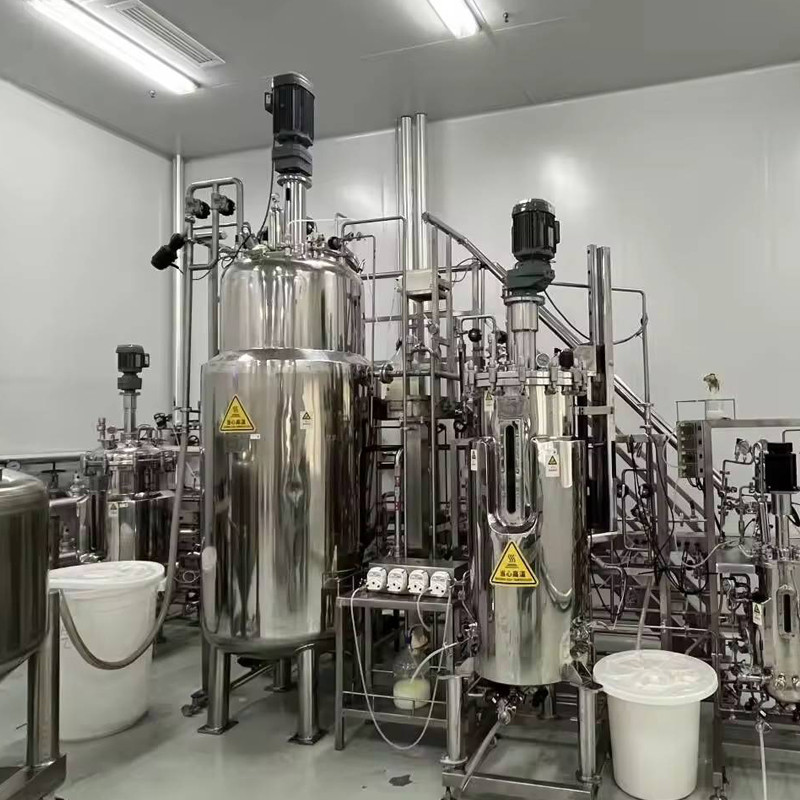
Those precious varieties that are scarce and difficult to find, and whose effects are difficult to absorb, can not only be mass-produced but also make the effective ingredients more useful through precise regulation in the fermentation tank.
1、 The old problem of liquid fermentation of Sanghuang: wild ones are almost impossible to dig up, and artificial planting takes 3-5 years. Even if they are grown, it is particularly difficult to extract polysaccharides and flavonoids from them, and the dissolution rate is so low that it is worrying.
Liquid fermentation is aimed at addressing these issues, with the core use of "secondary dynamic regulation":
The first step is to cultivate mycelium in a seed jar using common potato glucose medium (PDA) for 3 days to obtain highly active mycelium;
The second step is to forward the fermentation tank and add birch sawdust extract - simulating the growth environment of mulberry yellow in the wild, supplementing with 0.1% amylase (50000 μ/g) to help decompose nutrients. Finally, it was measured that polysaccharides and flavonoids were more than 30% higher than traditional planting.

And the entire process is sterilized with steam at 121 ℃ for 30 minutes, so there is no need to worry about bacterial contamination. Finally, it is made into a freeze-dried powder with over 90% retained activity.
Nowadays, many anti-tumor adjuncts and liver protection drugs contain it, and finally there is no need to focus on rare wild Sanghuang anymore.
How to combine 9 types of fermented traditional Chinese medicine and 8 core microbial strains to achieve reduced toxicity, increased efficiency, and better absorption?
2、 How difficult was liquid fermentation of Dendrobium before? It needs to be attached to the tree for planting, and it takes 3-5 years to harvest. The wild ones are almost gone.
Even more troublesome is that when boiled and consumed directly, the polysaccharide molecules inside are too large for the body to absorb much.
Liquid fermentation follows a one-stop approach of "tissue culture+fermentation", which directly solves the problem:
Firstly, good seedlings are required, so small tissues of 0.3-0.5mm are taken from the tip of Dendrobium officinale stems and cultured in a medium supplemented with banana puree (100g/L);
Then enter the fermentation tank and use a culture medium of "sucrose+peptone+banana puree" - sucrose provides energy, peptone supplements nutrients, and banana puree continues to simulate the field epiphytic environment.
The most crucial thing is that fermentation breaks down dendrobium polysaccharides into small molecules of 2000-5000 Da, which used to absorb only 20% when boiled and drunk, but now can reach over 60%.
Whether it's making nourishing drinks or anti-aging skincare products, they are both effective without damaging wild resources.

3、 Liquid fermentation of Poria cocos: The problem of adding "spleen strengthening holy medicine" to complementary foods may not have been noticed: Poria cocos needs to be buried in the soil for 3-5 years, and when dug out and boiled in water, the effective ingredient dissolution rate is less than 15%. Previously, it could only be used as a traditional Chinese medicine decoction piece, which was relatively limited.
Liquid fermentation solves these problems by "adjusting nutrients in stages", and the idea is very clear: in the first 0-5 days, let the mycelium grow quickly - using a high carbon to nitrogen ratio culture medium, maintaining sufficient oxygen at 26-28 ℃, the mycelium grows quickly, and then more effective ingredients can be produced later;
In the later 6-12 days, we will switch to the "catalyst" - adjusting the carbon to nitrogen ratio to 3:1 and adding a "catalyst" to allow the mycelium to synthesize more polysaccharides and triterpenes.
Here's a clever trick: the mycelium produces Poria cocos polysaccharide enzyme, which can break down large polysaccharides into small molecules smaller than 10000Da. This not only increases the extraction efficiency by 5 times, but also facilitates absorption.
Nowadays, not only can it be used as a spleen strengthening medicine, but it can also be mixed with probiotics and even made into children's complementary food powder, which can be used by the whole family.

4、 Ginseng liquid fermentation: afraid of overheating or too expensive? The pain points of ginseng are too obvious: one gram of wild ginseng costs thousands, which ordinary people cannot afford to eat; Even if they can afford it, many people are prone to getting angry after eating it, and those with sensitive constitutions dare not touch it.
The core of liquid fermentation is "microbial assisted conversion of ingredients", which is both cost-effective and gentle:
The first one used is ginseng beard root - a part that no one used to want before, now turned into treasure and reduced costs;
Then, recombinant Pichia pastoris was added, which can specifically produce β - glucosidase to break down the large molecular saponins (such as Rb1 and Rc) in ginseng into small molecules Rh2 and Rg3- these two small molecular saponins not only do not ignite, but also have higher activity.
The entire process is incubated at 25-28 ℃ and pH 6.0-6.5 for 48-72 hours, monitored by HPLC to ensure that the proportion of small molecule saponins exceeds 60%.
In the end, the cost is only 1/10 of wild ginseng (about 1.3 yuan per gram), which can be made into ready to eat ginseng slices and functional drinks. Workplace workers can chew two slices after overtime to replenish energy without worrying about overheating.

5、 Cordyceps liquid fermentation: Good products can be obtained in 15 days. Natural cordyceps only grows in high-altitude areas and is difficult to dig up, costing thousands of yuan per gram; What's even more frightening is that some even contain heavy metals, making it difficult to eat with peace of mind.
The idea of liquid fermentation is to simulate a high-altitude environment in a tank, which is safe and inexpensive:
We use Cordyceps militaris, which is closely related to natural Cordyceps and contains the same active ingredients;
During fermentation, the temperature is deliberately controlled: 20-22 ℃ during the day to allow the mycelium to grow, and 12-15 ℃ at night to simulate the temperature difference between day and night on the plateau, so that cordycepin can be synthesized more; Finally, after being subjected to a low temperature of 10-12 ℃ for 24 hours, the adenosine content can reach over 0.15%.
The culture medium is also simple, and the mycelium can be harvested in 15-20 days.
Tested, cordycepin, adenosine and natural cordyceps are similar, and have also passed heavy metal testing.
When it is made into nutritional granules, the price is only 1/20 of that of natural cordyceps. It is convenient for middle-aged and elderly people to add it to Congee in the morning to supplement their immunity.