Inventory the top 20 most common and popular biological reaction products! Smeaglutide, ergothionein, astaxanthin, and biofertilizer ..

In bioreactors (fermentation tanks), substances produced through microbial fermentation or cell culture cover multiple fields such as medicine, food, energy, and chemical engineering. The following are 20 common products and their application scenarios.
The production of these substances relies on precise control of the fermentation process by bioreactors, such as dissolved oxygen, pH, temperature, and nutrient supply, to achieve high yield, high efficiency, and low cost.
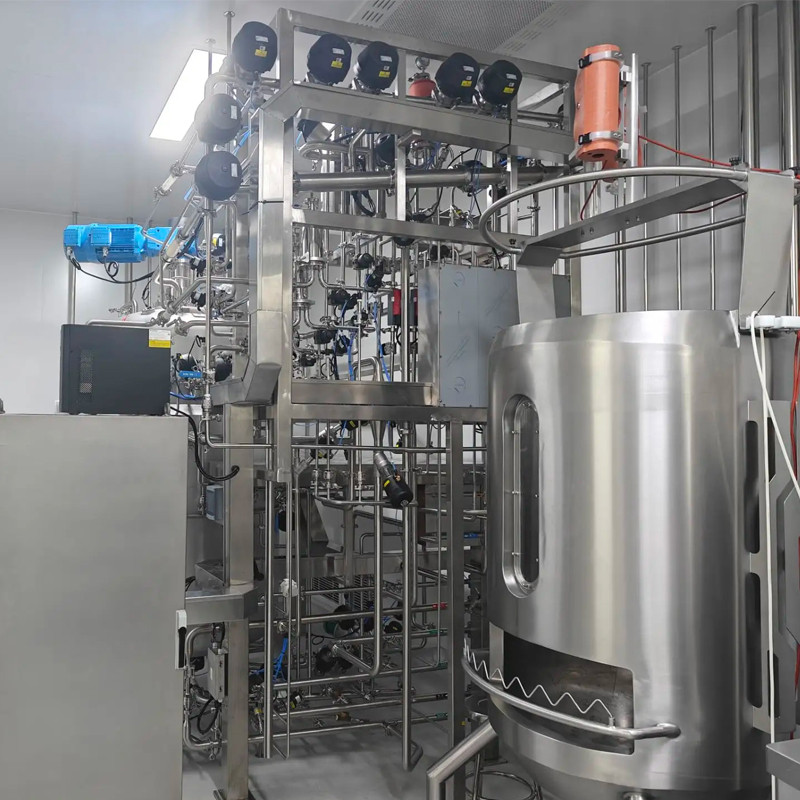

一、 Pharmaceutical and Biological Products
1. Penicillin
Produced by fermentation of Aspergillus flavus, it is the first industrialized antibiotic. Broad spectrum antibacterial treatment for Gram positive bacterial infections is the cornerstone of modern antibiotics.
2. Insulin
Escherichia coli or yeast modified through genetic engineering (such as brewing yeast)
Mother expresses recombinant insulin in a bioreactor. Treat diabetes and regulate blood sugar level.
How strong is semaglutide? Global sales surged by 38%, and behind China's 75% growth rate, 30 companies are competing for 30 tons of production capacity!
3. Interferon
Recombinant Escherichia coli or mammalian cells (such as CHO cells) for fermentation production. Antiviral, anti-tumor (such as chronic hepatitis B, leukemia), regulate immunity.

4. Cefotaxime antibiotics (such as cefotaxime)
Fermentation of cephalosporin fungi and optimization of activity through chemical modification. Broad spectrum antibacterial, effective against penicillin resistant bacteria, used for respiratory and urinary system infections.
5. hepatitis B vaccine
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae or CHO cells express hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in bioreactor. Preventing hepatitis B virus infection is a basic vaccine widely available worldwide.
6. Hyaluronic acid (HA)
Streptococcus genus (such as Streptococcus equi) is fermented or synthesized by genetically engineered bacteria. Medicine (joint lubrication, wound repair), cosmetics (moisturizing), medical aesthetics (fillers).
7. Monoclonal antibodies (such as rituximab)
Hybridoma cells or CHO cells are cultured in animal cell bioreactors. Treat cancer (such as lymphoma) and autoimmune diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis).

二、 Food and additives category
8. Ethanol (alcohol)
Brewing yeast ferments starch (corn, wheat) or sugar (sugarcane, waste molasses). Beverage liquor (Baijiu, beer), fuel ethanol (bio gasoline additive), chemical raw materials.
9. Citric acid
Aspergillus niger ferments glucose or sucrose, the world's largest organic acid production. Food acidifiers (beverages, jams), detergents (chelating agents), pharmaceuticals (anticoagulant adjuvants).
10. Glutamic acid (raw material of monosodium glutamate)
Glutamate rod-shaped bacteria ferment glucose or starch hydrolysate. Food flavoring agent (MSG), feed additive (promotes animal growth).

11. Lactic acid
Lactic acid bacteria (such as Lactobacillus) or Rhizopus oryzae ferment carbohydrates. Monomer raw materials for food preservation (acidifiers) and biodegradable plastics (PLA).
12. Lysine
Fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum or Corynebacterium flavum. Feed core additives (to compensate for the deficiency of lysine in grains and promote the growth of livestock and poultry).
13. Vitamin B12
Propionibacterium (such as Propionibacterium Xie) or Streptomyces are used for fermentation. Food fortifiers (milk powder, nutritional supplements), pharmaceuticals (treatment of megaloblastic anemia).
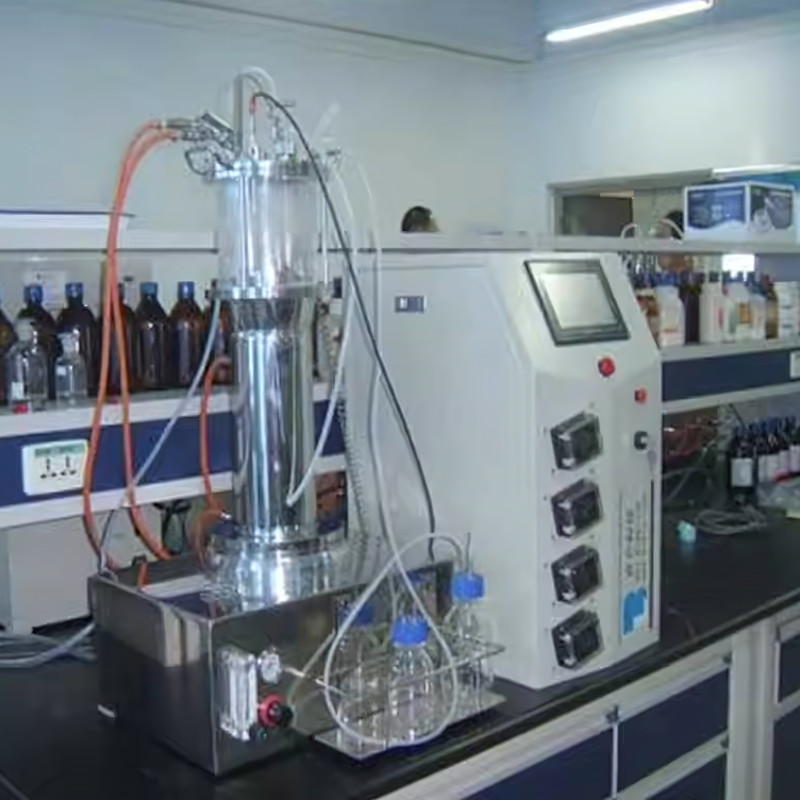

三、 Industrial enzymes and chemical categories
14. Alpha amylase
Fermentation by Bacillus subtilis or Aspergillus oryzae. Starch processing (sugar production, beer saccharification), textile desizing, detergent (decomposition of starch stains).
15. Protease
Fermentation by Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus oryzae or yeast. Food processing (meat tenderization, cheese ripening), detergents (breaking down protein stains), leather depilation.
What are the advantages of bio fertilizers ranging from 4.35 billion to 2 million tons? Starting from scratch, we will help you build a production line!
16. Cellulose enzyme
Fermentation with Trichoderma reesei or Trichoderma reesei. Biomass hydrolysis (conversion of straw to ethanol), feed digestion (improvement of crude fiber utilization), papermaking and pulp making.
17. β - carotene
Red haired yeast (Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous) or engineered bacteria fermentation. Food coloring (artificial butter, beverages), nutritional supplements (vitamin A precursors), feed additives (poultry egg yolk coloring).

四、 Energy and Environmental Protection
18. Methane (biogas)
Methanogenic bacteria (such as Methanococcus) decompose organic matter (straw, sewage) in anaerobic bioreactors. Clean energy (cooking, power generation), reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
19. Biodiesel (microbial oil)
Oil producing yeast (such as Yersinia lipolytica) or algae accumulate oil in a bioreactor and produce it through ester exchange. Replace fossil diesel with renewable energy.
20. Bt toxin protein (biopesticide)
The fermentation of Bacillus thuringiensis produces crystal protein (Cry protein). Non polluting pesticides are used to control Lepidoptera pests (such as cotton bollworm) and reduce the use of chemical pesticides.