Why is medical beauty booming, but the fermentation process is difficult to die? Analyze the 4 core bacterial strains and 3 major bottlenecks!

In the medical beauty and health industry, biological reaction strains are widely used in raw material production, skincare product research and development, and medical scenarios through technologies such as biological fermentation and metabolic regulation.
1. Escherichia coli
As an important chassis strain for industrial fermentation, Escherichia coli is used to produce various medical beauty active ingredients.
For example, genetically engineered Escherichia coli can efficiently synthesize recombinant collagen, which expresses type III collagen with low immunogenicity and high biocompatibility, and is widely used in skin repair and anti-aging products.
In addition, E. coli is also used to synthesize polyphenolic compounds such as salidroside and ferulic acid, which have antioxidant and whitening effects and are added to functional skincare products.

2. Yeast (such as Pichia pastoris)
Yeast exhibits outstanding performance in recombinant protein production. Pichia pastoris is used to produce high-purity recombinant humanized type III collagen, with a shake flask yield of over 1g/L and significant industrial fermentation potential.
In addition, yeast can synthesize terpenoids such as squalene and retinol through metabolic engineering, which play important roles in antioxidant and skin metabolism regulation.

3. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
In the field of skincare products, lactic acid bacteria regulate the skin's microbiota by secreting lactic acid and antimicrobial peptides, inhibiting harmful bacteria such as Propionibacterium acnes, while promoting stratum corneum renewal and improving skin barrier function.
Oral supplements: Bifidobacterium improves skin health indirectly by regulating gut microbiota, and its metabolites short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) can enhance immune regulation of the gut skin axis and reduce inflammatory reactions.

4. Clostridium botulinum
Traditional botulinum toxin production relies on fermentation and extraction of botulinum toxin, but there is a risk of endotoxin contamination.
The new recombinant technology expresses high-purity botulinum toxin protein through strains such as Escherichia coli, which solves the problem of biosafety from the source and has higher stability and safety.
Although the application of bioreactors in the field of medical aesthetics and health has broad prospects, the transition from laboratory to commercialization requires overcoming multiple challenges such as technical bottlenecks, safety barriers, and regulatory obstacles. These issues are particularly prominent in new application scenarios

Efficiency bottleneck of functional bacterial strains
The fermentation yield of new active ingredients is generally low, such as the production of miRNA engineered bacteria targeting anti-inflammatory effects, which only reaches the microgram level, far below the gram level required for industrialization;
The fermentation efficiency of uric acid synthesis bacteria is only 0.8g/L, resulting in a raw material cost that is 5-8 times higher than traditional chemical synthesis.
In addition, the stability of the strain is insufficient - the symbiotic cycle between Lactobacillus reuteri and brewing yeast in the synthetic bacterial community only lasts for 72 hours, which can easily lead to microbial imbalance and affect product consistency in the future.
Difficulties in scaling up the process
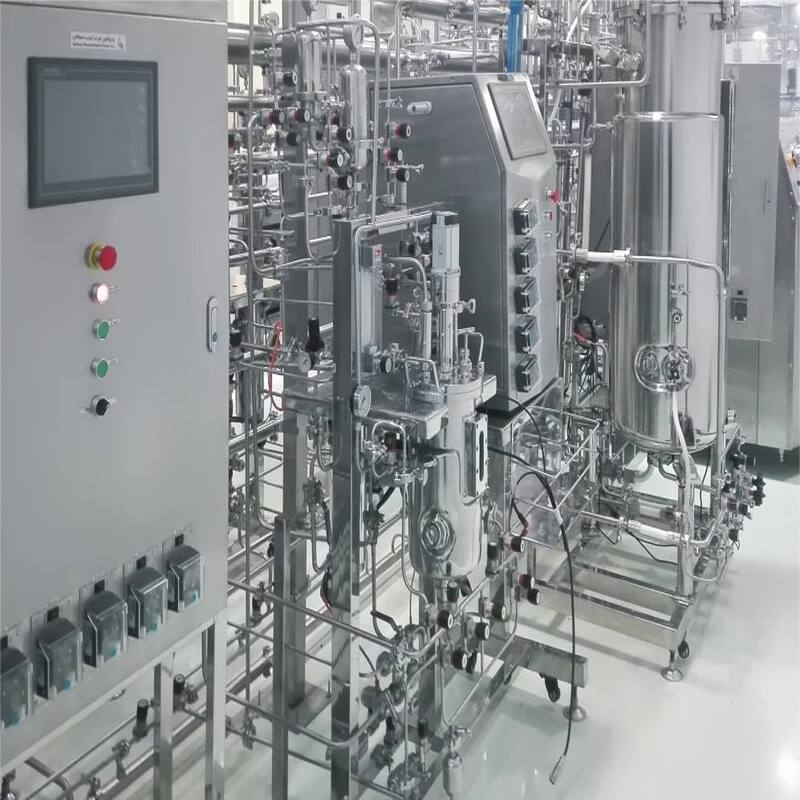

The optimization parameters of laboratory shake flasks or small fermentation tanks are difficult to directly transfer to industrial production. For example, when producing recombinant collagen with Pichia pastoris, the difficulty of controlling dissolved oxygen in a 500L tank suddenly increases, resulting in a 30% loss of product activity;
When acetic acid bacteria synthesize bacterial cellulose, stirring at a speed exceeding 150rpm can damage the three-dimensional structure of the nanofibers, while low-speed stirring can cause local anaerobic reactions and pose a risk of bacterial contamination.
Amplification of fermentation process

Obstacles to precise regulation of metabolic pathways
The complexity of bacterial metabolic networks often leads to "byproduct interference". When soil bacteria ferment fucoidan, about 20% of the carbon source will be diverted to unrelated metabolic pathways, generating ineffective polysaccharide impurities;
When modifying lactic acid bacteria to produce uric acid, overexpression of key enzymes can cause cellular stress, which in turn inhibits growth rate.