From royal jelly to anti-aging technology: How does the world's first synthetic biological royal jelly acid rewrite the skincare landscape?

In royal jelly, there is a mysterious component called "longevity factor" - royal jelly acid (10-HDA).
This unsaturated fatty acid, which accounts for only 1.4-2.4% of royal jelly, is considered the "golden ingredient" of high-end skincare products due to its multiple effects such as anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant.
But for a long time, the extremely low yield and high cost of natural extraction (1 gram of natural royal jelly acid is as expensive as 1 gram of gold) have kept it stuck in laboratories and niche markets.
It was not until 2025 that royal jelly acid was broken through the industrial production of "window paper" by synthetic biotechnology, achieving large-scale production for the first time.
Traditional vs. synthesis: natural extraction related to "efficiency and cost"
The traditional method of extracting royal jelly acid from royal jelly requires the consumption of tens of kilograms of royal jelly to obtain 1 gram of active ingredients, and is significantly affected by season and bee species, resulting in highly unstable yields. In addition, natural extracts are often accompanied by protein impurities, which can easily cause sensitive muscle irritation.
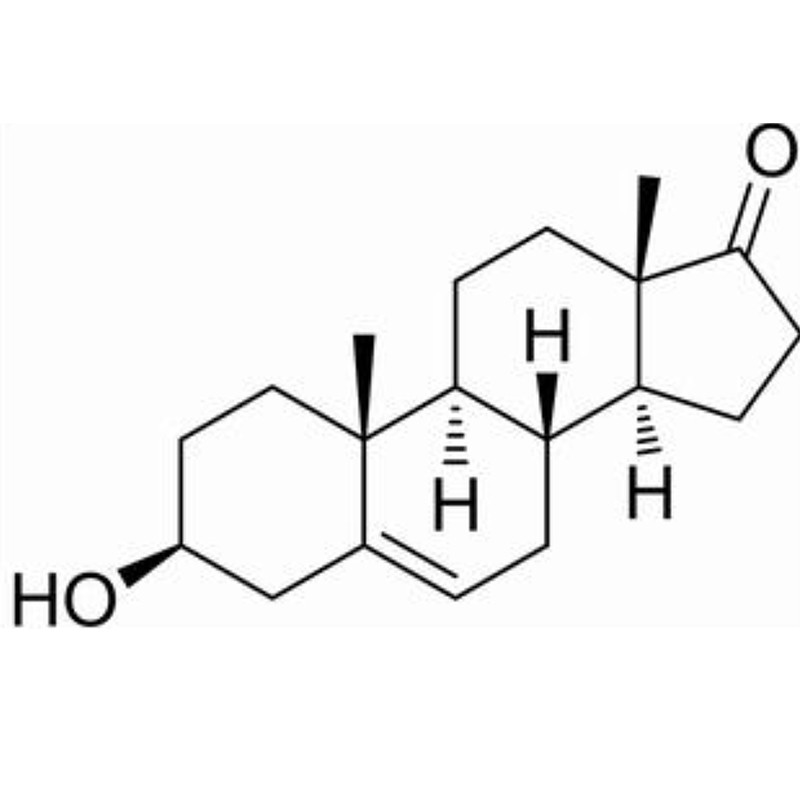
Chemical synthesis
The early chemical synthesis route required more than 8 steps of reaction, which not only produced a large number of by-products and isomers, but also made purification difficult, resulting in a yield of less than 30%, and the risk of residual chemical reagents was difficult to avoid.

Synthetic biology
By deciphering the molecular mechanism of royal jelly acid synthesis and introducing key genes into "chassis cells" such as Escherichia coli, an engineering strain capable of efficiently synthesizing royal jelly acid was constructed.
In bioreactors, these "micro factories" use glucose as raw material and achieve large-scale production of royal jelly acid through high-density fermentation technology (with bacterial concentration more than 10 times that of traditional processes).
Finally, combined with GEW high-purity extraction technology, royal jelly acid with a purity of over 98% was produced, reducing the cost by more than 80% compared to natural extraction.
How to produce synthetic royal jelly acid?
1. Gene editing
Select key enzyme genes involved in the synthesis of royal jelly acid (such as acyltransferase genes), and introduce them into Escherichia coli through genetic engineering technology to create an exclusive "production strain".
2. In a bioreactor
precise temperature control is achieved pH、 Parameters such as dissolved oxygen allow engineering bacteria to produce royal jelly acid in the optimal environment. This step is like synchronizing the operation of countless micro factories inside a tank, with a daily output that can reach thousands of times that of traditional processes.
3.GEW purification
uses membrane separation and chromatography technology to remove bacterial residues and metabolic waste from the fermentation broth, retaining only highly active royal jelly acid molecules, and ultimately obtaining almost pure white crystals.